
What is Computer vision?#
Background#
In the digital world, scientists are working hard to create machines and robots that can interact with humans the way humans interact with each other. You cannot interact with another human being around if you are not aware of the objects and background around you. There are many ways to know the things around us. We can know them through smell; without looking anything around we can tell, here is a rose flower or samosa or sugar factory around. Without looking we can tell whether a train is coming or going, a person is going or coming, this is a song sung by Lata Mangeshkar. Without looking I can tell this is smooth or rough, hard or soft, cold or hot. In all these cases we could identify the objects and things around us without using our eyes.
But the truth of life is, we know most of the things around us just by looking. Even if we can smell, till the time we don’t see we don’t believe in the existence of things. That is why there is a saying in English “Seeing is Believing”. So, vision is a very important part of human survival ands human interaction with the environment around him. Thus, if we want to create machines or robots which are environmentally aware then they should have the ability to see, the vision. If a machine can see and understand the objects in the environment then we can say a computer has vision, Computer Vision.
How Computer Vision Works?#
Human Vision#
You may be thinking we see through our eyes, therefore if a machine has a camera installed on it will be able to see. But, this is not true. The eyes are an important part of our seeing process but the process of seeing is very complex. Subjects like optical physics, vision science, psychophysics, Opthalmology, and brain science deals with the process of seeing. With the help of eyes functions and brain functions, vision happens in the human brain. Eyes are not only what we see on the surface, but there are also complex layers combined that form a biological machine called an eye (human in-built camera). But after seeing a rose flower, the camera is not aware that it is a rose flower, no matter how many years that camera is exposed to that rose flower. But, even a human child can identify anything simply by just one time looking or one-time training. The human brain is a very complex biological machine and it has some parts that deal with processing the signals which come inside the brain via vision channels (nerves/cables). The process of vision also involves association with existing knowledge, then only I can identify whether I have seen this thing earlier or it is a completely new thing for me. The process of storing vision data, searching vision data in the human brain, and analyzing the data happens at an extremely fast speed. For doing this work energy come from oxygen and blood circulation.
Who sees the seen?#
This is a philosophical question, but it is worth touching on. When the eyes get reflected light from objects say a rose, the brain processes the light signals and finally through a complex process identifies the object from which light reflects, it is a rose. Here who is helping me to see? My eyes and my brain. But, who is seeing (means who is the seer of the seen)? This answer is difficult to answer and philosophers and scientists have a long unending debate around this. Science says the human brain sees. Philosopher says then who is seeing that part of the brain which is experiencing that “I am a seer”? Is that seer locatable in the human brain, or the human body? Is it local? Can it be localized? First of all, does this seer has physical nature? If that is not physical then there is no question of localization.
What is physical? That which can be sensed through our physical senses or our scientific instruments. By this definition light is physical, the smell is physical, air is physical, and energy is physical. A few years back there was something that we couldn’t sense using our senses or our machines but today we can sense that because of our advanced technology. So a few years back what was non-physical became physical today? This is not how logic or science works. Truth is the truth always that does change because of time, space and situations. Is there anything, which is non-physical for always; keeping your future technologies in the mind? Emotions of love, hate, jealousy, etc are physical because you can measure them very well in the coming time. What about consciousness? Is it physical? But the question comes, what is consciousness? What is awareness? It is a complicated question and human beings of all time, philosophers, thinkers, and scientists keep dwelling on this subject and trying to answer this differently. Nowadays, the new sciences are gaining momentum and attraction from the intellectuals and thinkers of all religions, communities, and scientists of all the different streams. It is mind sciences. Just to remind you, brain sciences are different than mind sciences.
Computer Vision - How Visioning Happens in Machine#
Computer scientists took inspiration from brain scientists and they want to simulate the human brain and its working in computers. This gave rise to neural networks. Earlier, the term neural networks were referring to the human brain, nowadays when people are discussing neural networks they are discussing about computer neural networks. A computer neural network has multiple layers as a human brain has, each layer has multiple neurons (like a human brain, a human brain has approx 100 billion neurons in it), but all the brains are not active all the time. Based on the input certain neurons become active in some parts of the brain. What neuron will become active by seeing what or listening to what, this is all part of human training, heredity, and human brain design? Some of that is in our control and some is not. Similarly what neurons will be activated in the next layer of the computer neural networks depends upon what activation function is used, and what input has come. There are many activation functions and many kinds of layers. When an image is given to a computer, it is nothing but a bunch of pixels for the computer. Each pixel is one byte so it can have a value between 0 to 255. When a 16-megapixel camera captures a photo then the image has 16 megapixels. More the pixels, the better the quality of the image. We have sharper contours between different objects in the image. When these 16MB images are given to a computer neural network, and they go through different layers then different layers do different work. But ultimately all the layers are identifying different features from the given image. These features can be contours, edges, regions of interest points, colors, and color intensity, in the case of a face (it may be eyes, nose, mouth, ear, forehead, lips, etc), in the case of a car (body, bonnet, headlight, number plate, window, mirror, glass, etc). Using these features computer can learn what is there in the image.
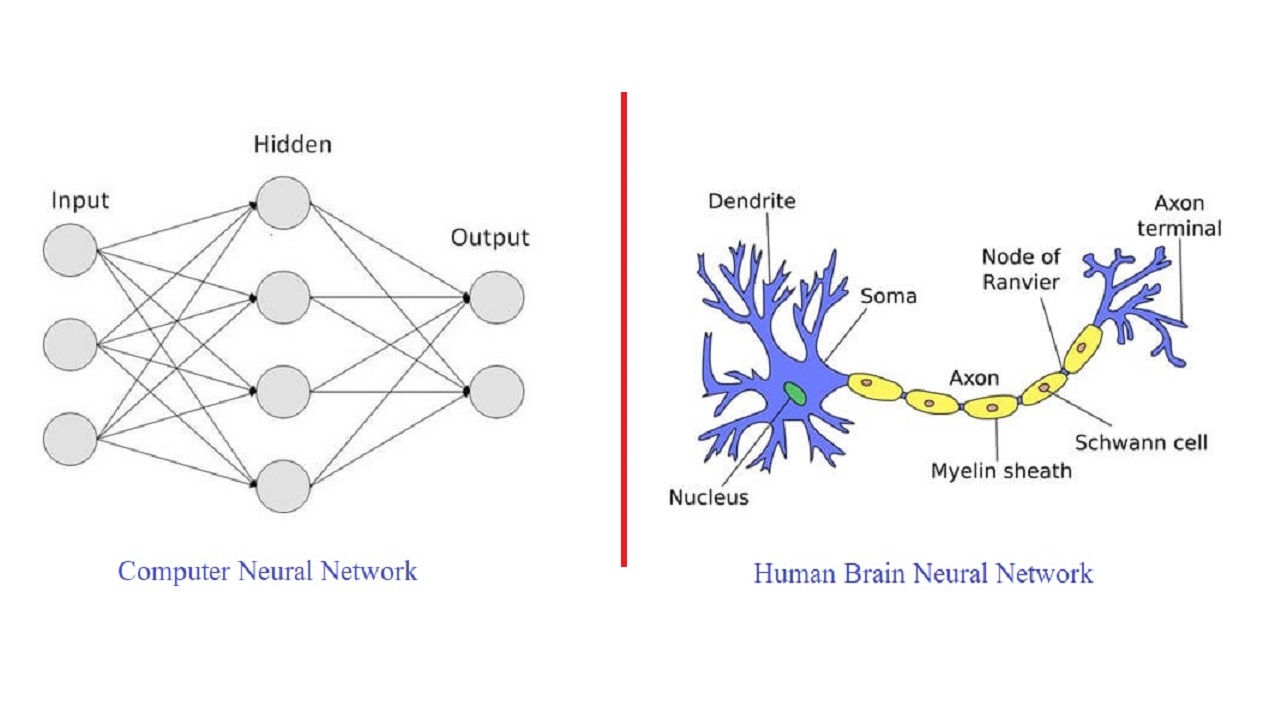
Human Neural Network vs Computer Neural Network
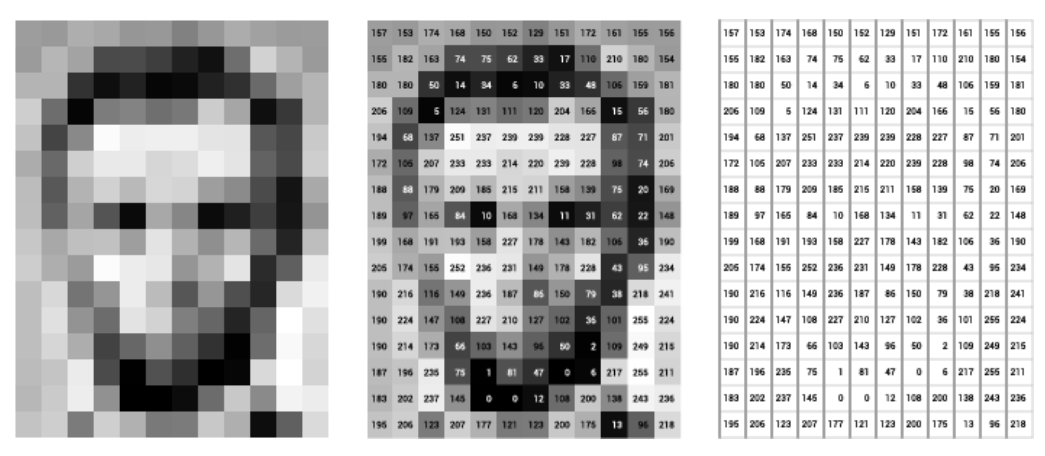
How Computer See an Image
How does Visioning happen in computers?#
To get the computer vision work done from a computer we need to input the image or video frames to a neural network. There are different kinds of neural networks. The architectures of these neural networks were created using some programming languages like python, scala, and java. After that, using input images these neural works are trained. Before the training of neural networks, the neurons and connection of the neural network have no weight & biases (W&B) or random W&B. During the training process these W&B are learned in such a way that whatever work a network is supposed to do, that work is done with minimum error. There are many kinds of layers in the entire architecture. Some common names for these are the convolution layer, deconvolution layer, recurrent layer, activation layer, dropout layer, pooling layer, dense layer, etc. Each of these layers has many variants. Depending upon the computer vision task these layers can be chosen in the architecture.
During the training pixel values of the input image are processed from left to right in the architecture. These numbers go through different layers and W&B are learned. When calculations are happening from left to right (input to output) this is called a feed-forward pass. But when calculations are happening from right to left that is called a backward pass. The purpose of a forward pass is the calculation of the gradients/slopes or learning W&B of the neuron, and the purpose of a backward pass is to update the old values of the W&B of these neurons. There are many techniques to perform these steps. During the training process, each image/frame is scanned multiple times. How many times all the images are scanned is called an epoch. During the training process, when will the training stop, this decision depends upon the data scientist. It can be decided based on the performance or accuracy results has been achieved, the number of times the image scan is done, or other parameters.
When training is complete, W&B has been learned by the neural network then we have a model ready. Now, this model can be used for the final prediction or performing the task for which we created the model.
Computer Vision Tasks#
- Image Classification

- Image Localization or Object Detection

- Semantic Segmentation
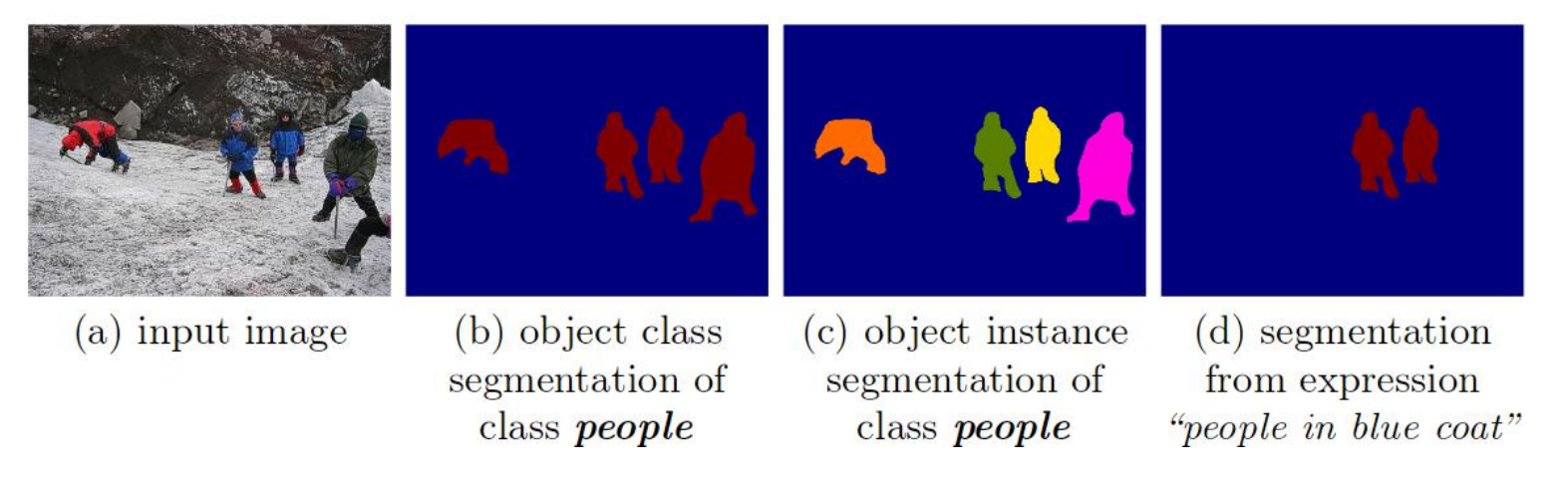
- Instance Segmentation
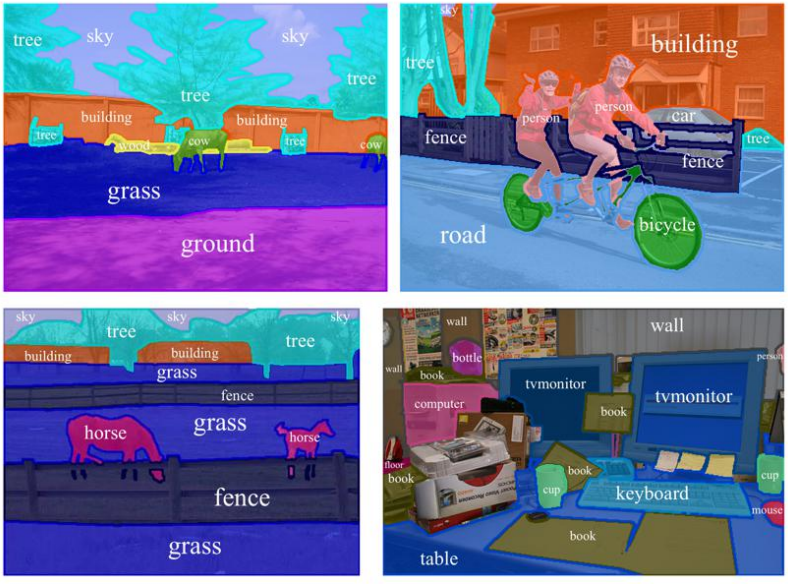
Source: Semantic Segmentation Presentation - Edge Detection

- Pose Detection
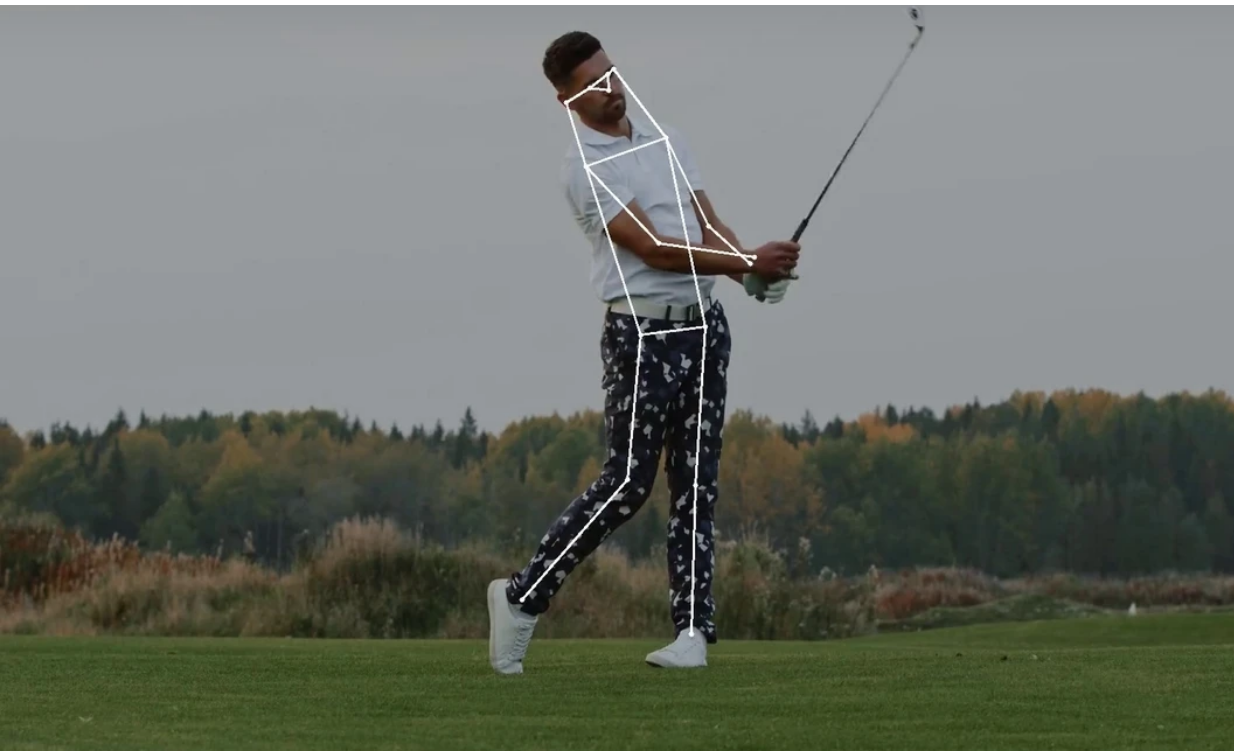

- 2d Pose Estimation
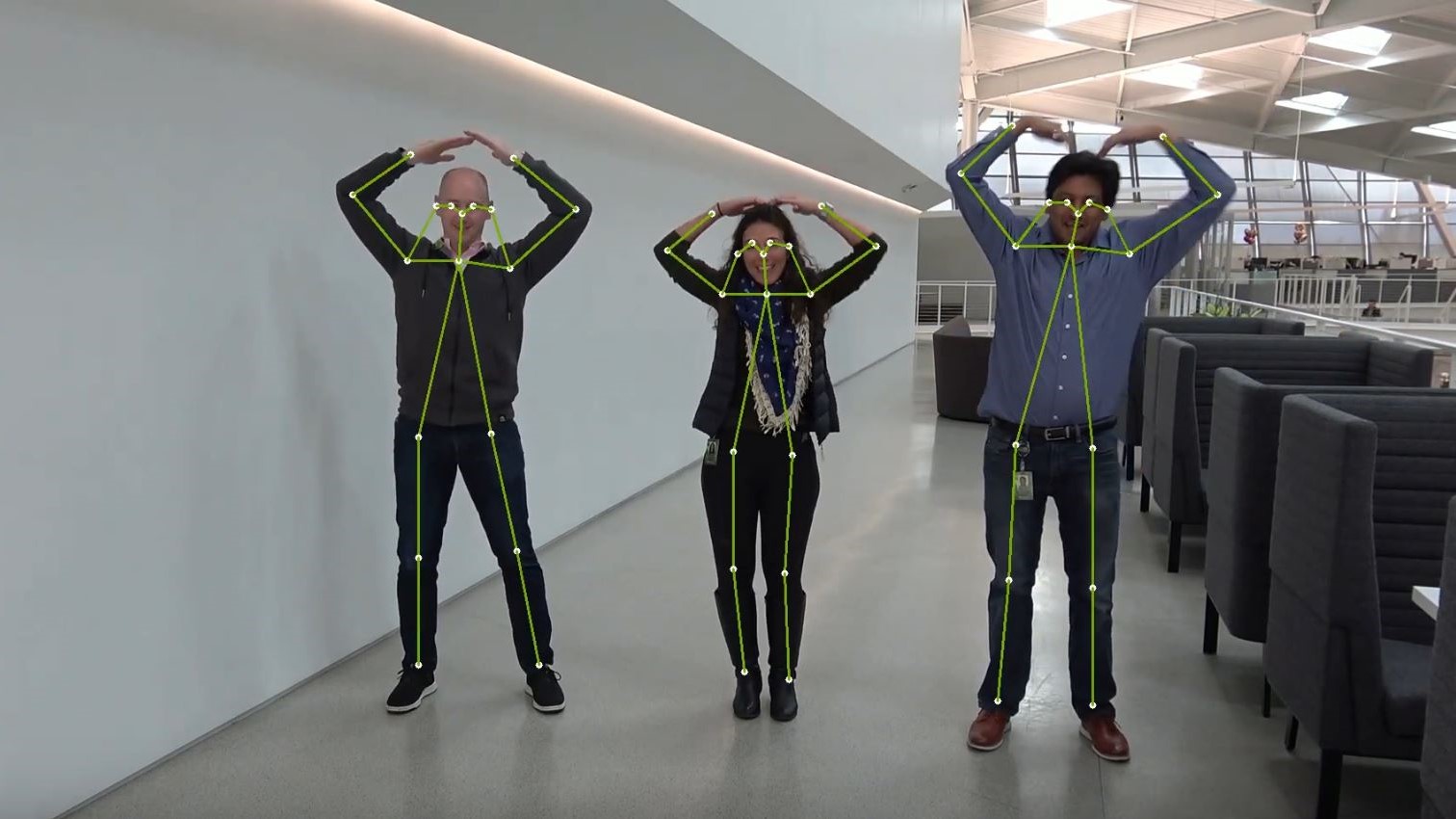

- 3D Pose Estimation
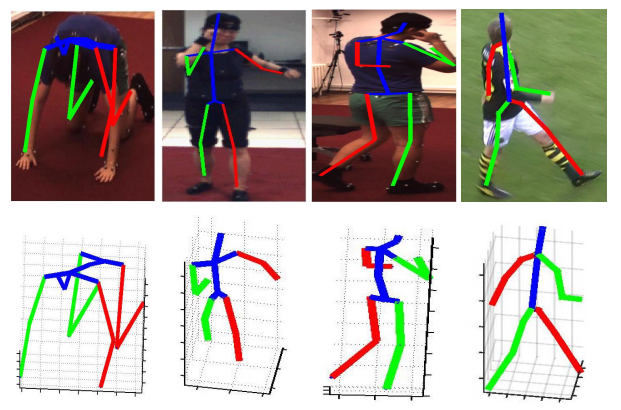
- Video motion analysis

- Image Restoration
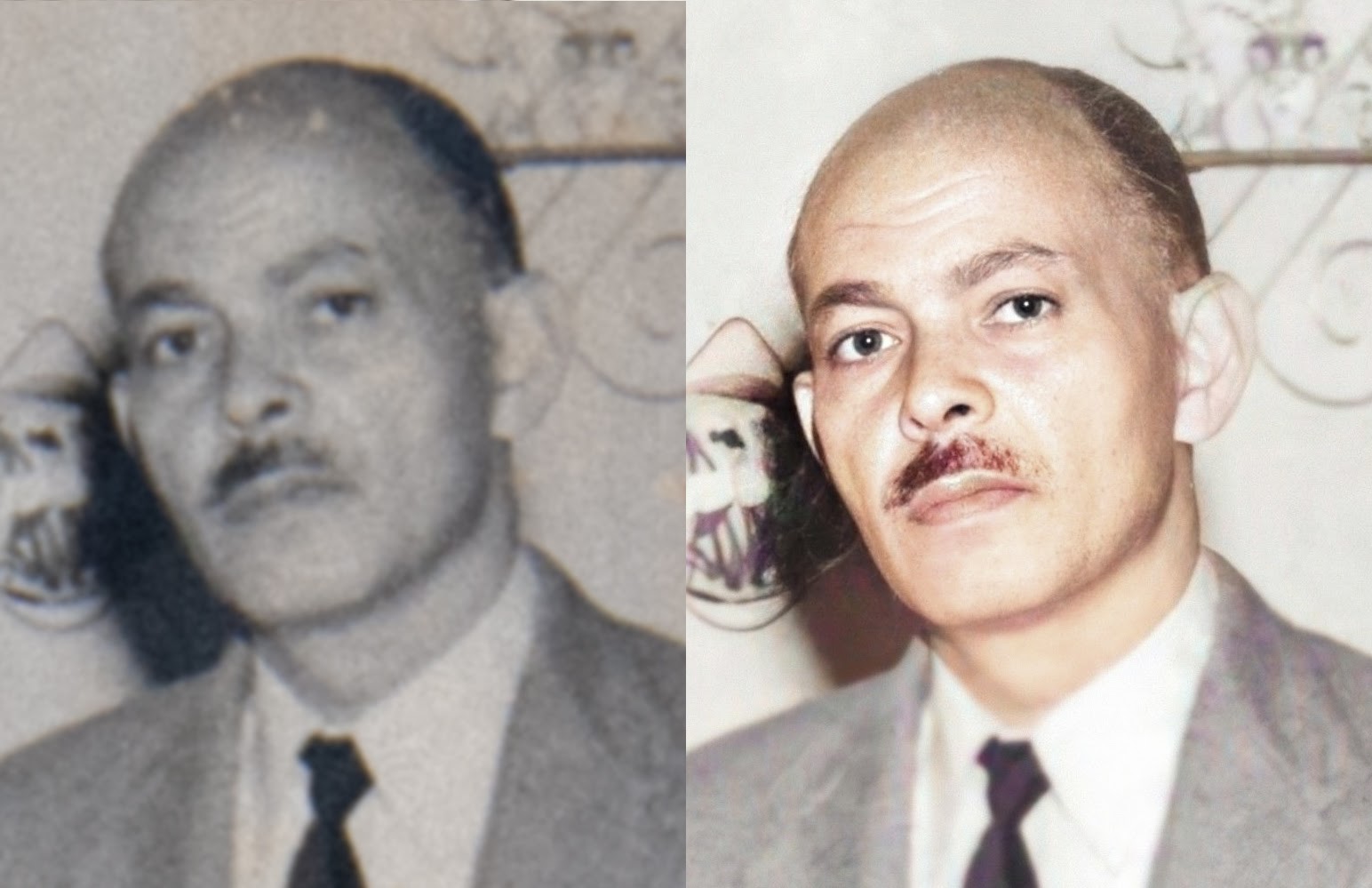

- Visual Relationship Detection : It is the ability to decipher what relationship does the two objects share
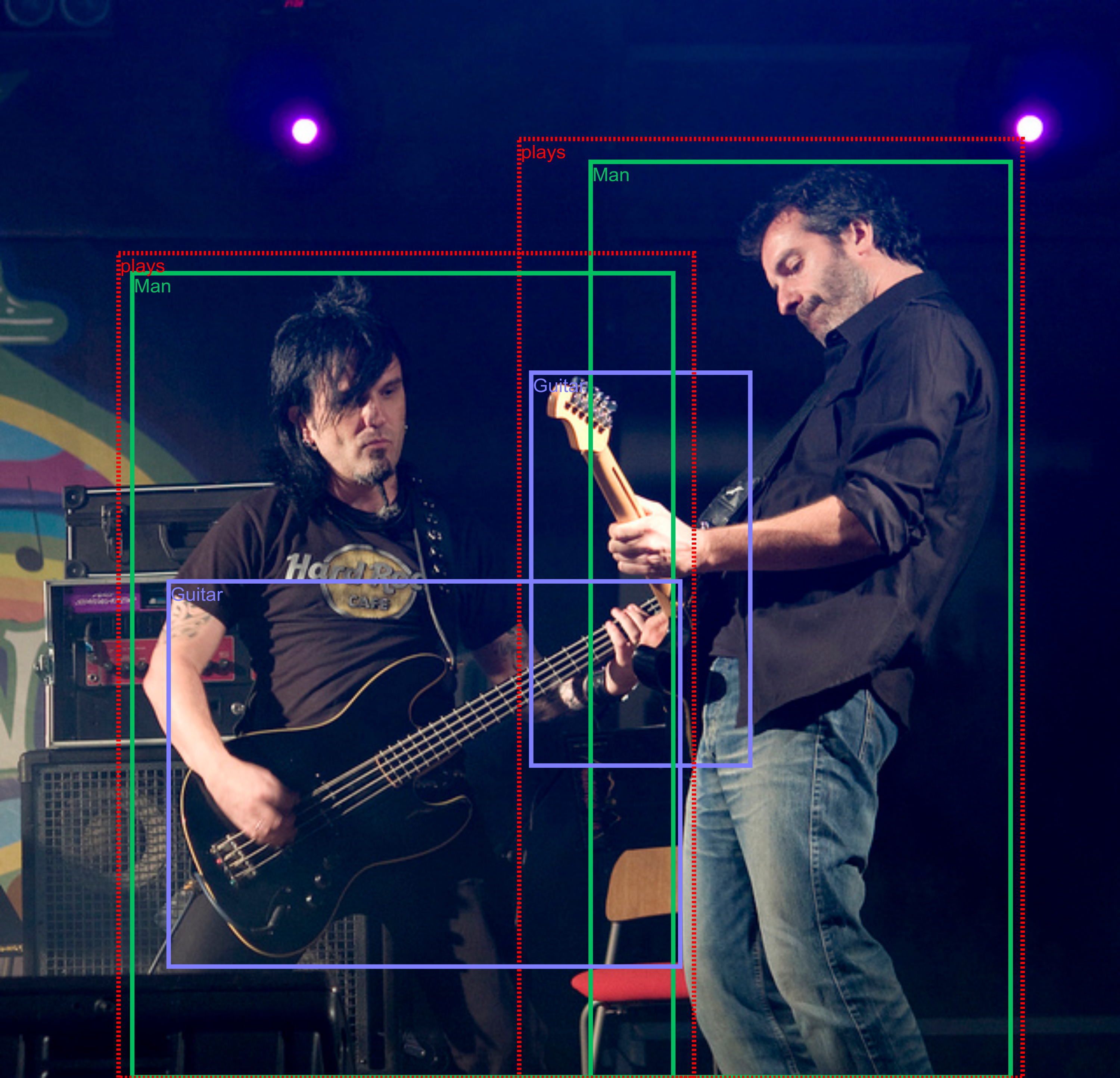
Source: Kaggle-Google AI - Image Reconstruction
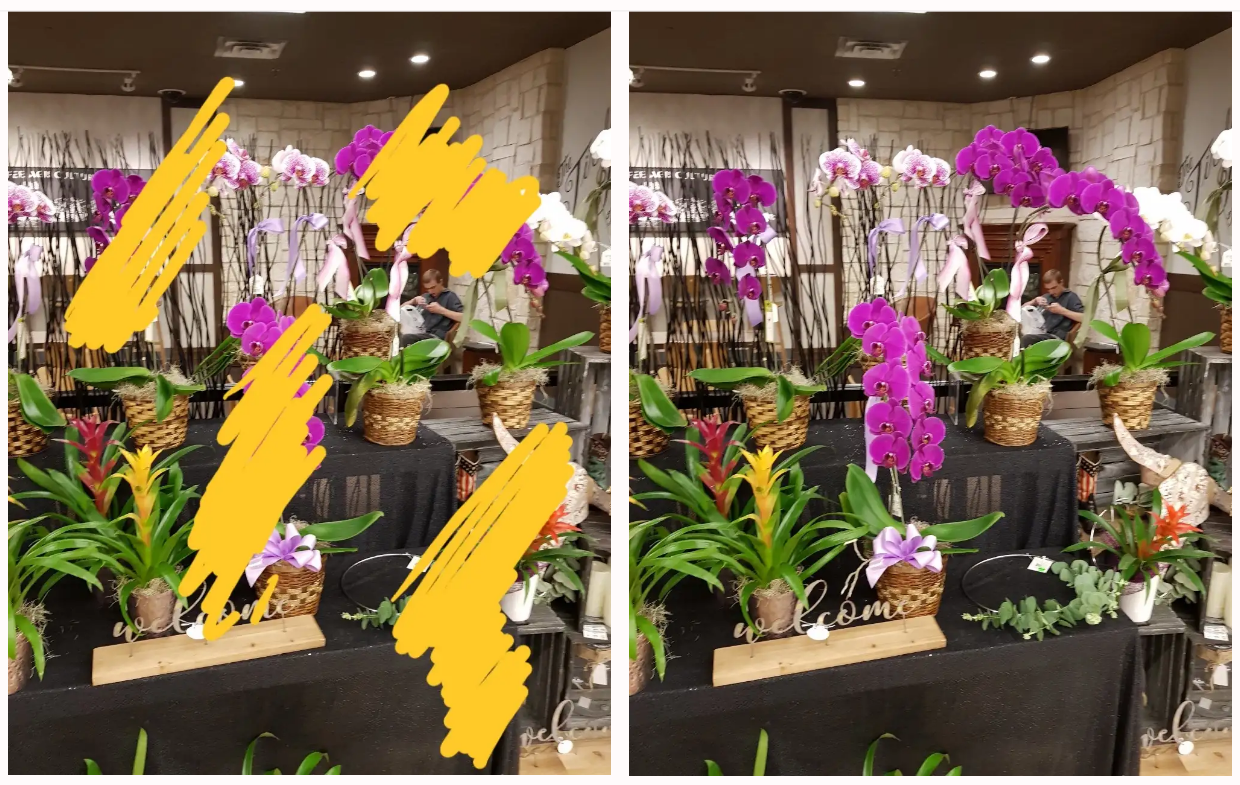

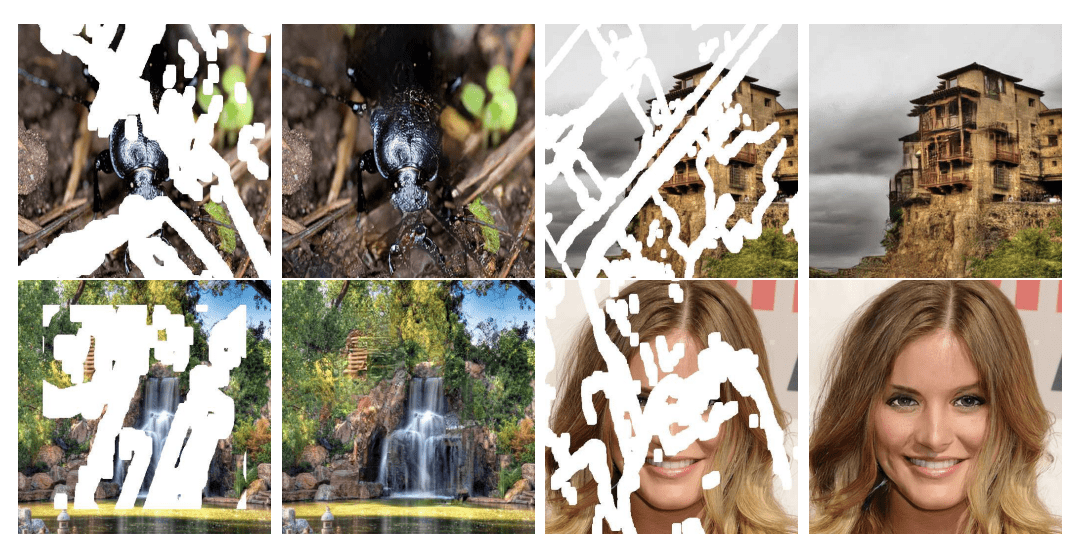
- Photo Inpainting

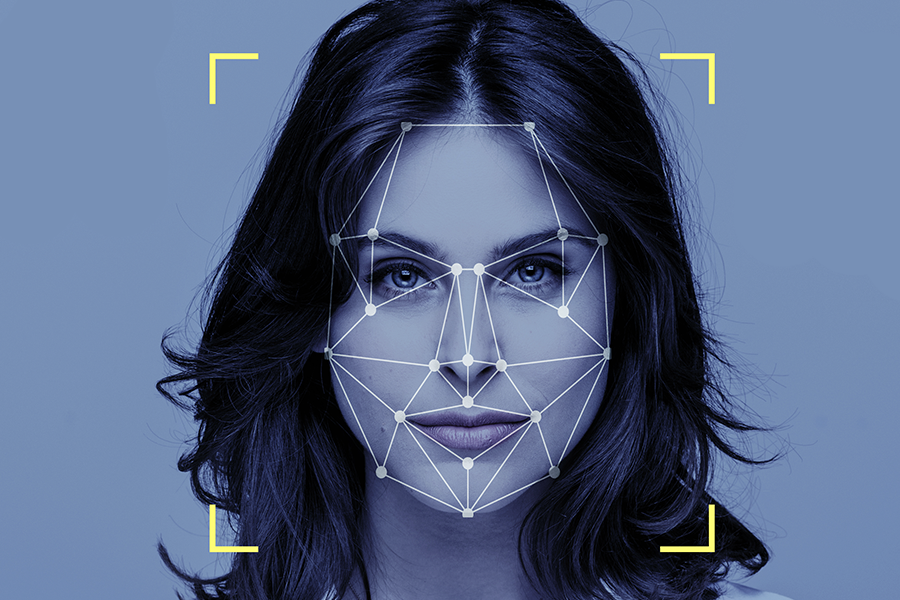
- Face Recognition

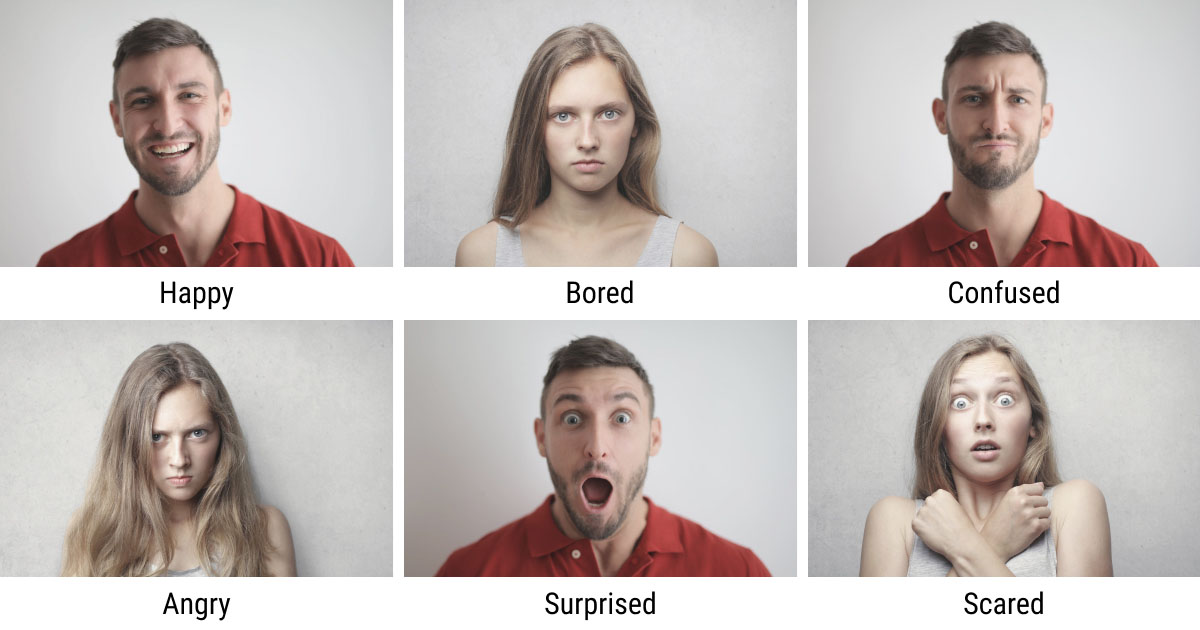
- Emotion Recognition

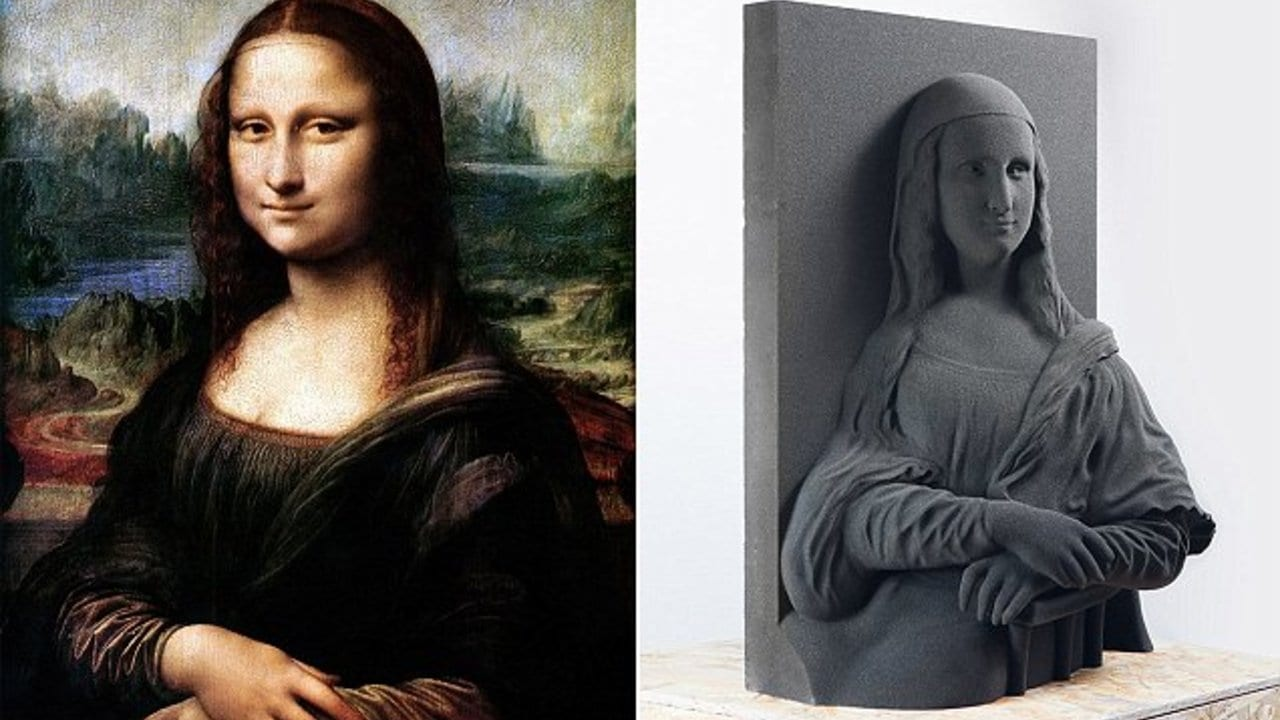
- 3D image construction from a photograph

- Image Style Transfer
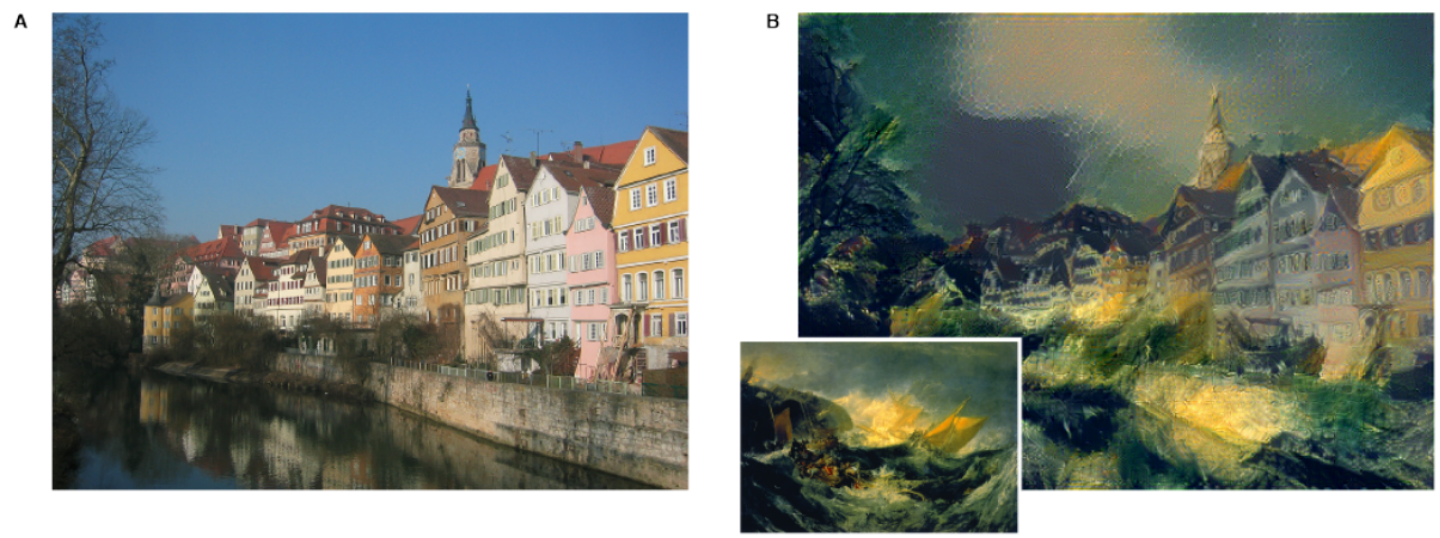

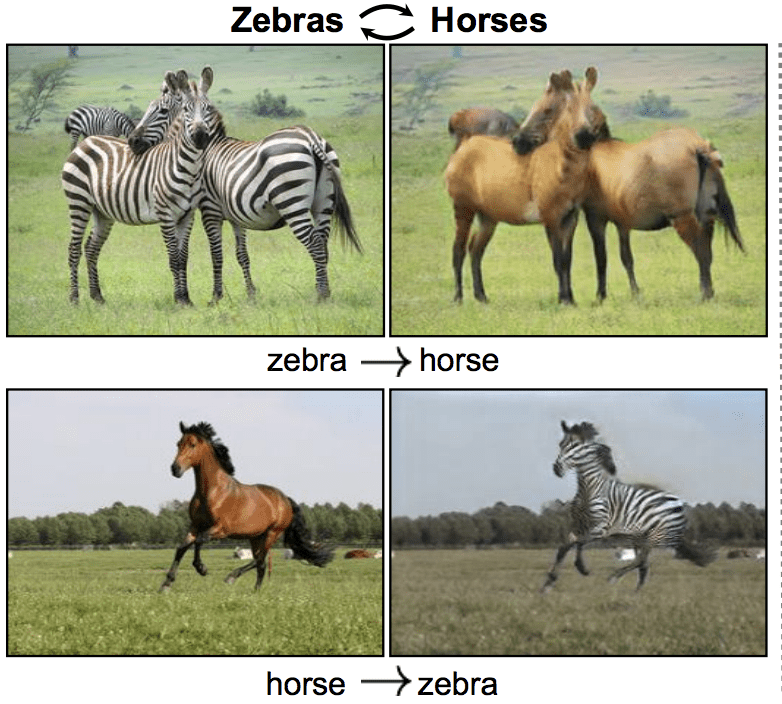
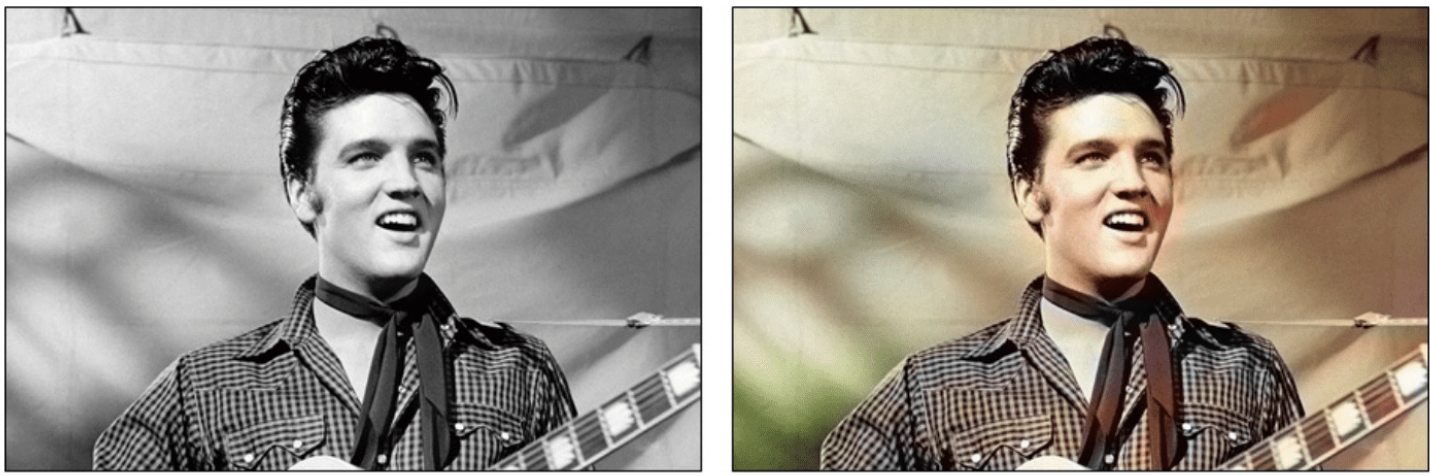
- Image Colorization

- Image Synthesis : Image synthesis is the process of artificially generating images that contain some particular desired content.
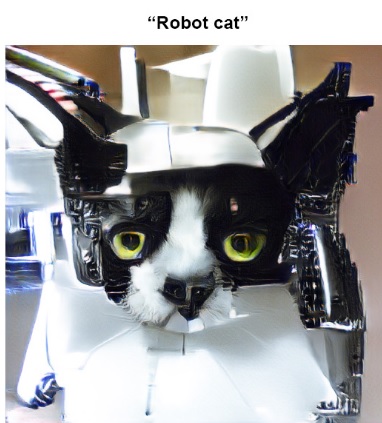
- Image Captioning

- OCR (Optical character reader)
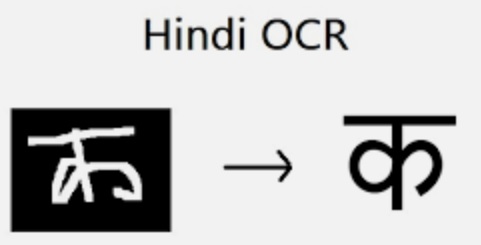
- Generating a textual description of an image
- Generating a textual description of each object in an image
- Synthesizing an image based on a textual description
- Tracking People and Vehicles
- Image Labelling/ Annotation Tool
- Video Tracking
- Art Generation
- Headshot Generator
- Photo Upscaler
- Object Remover
- Background Remover
- Art Personalizer
- Picture Colorizer
- Picture Restorer
- Face Enhancer
- Color Generator
- Social Distancing

Applications of Computer Vision#
Computer vision can be used as follows.
- In the field of human motion analysis like sports, medicine, intelligent video analytics, and physical therapy
- Manufacturing and to count and track microorganisms like bacteria and viruses.
- Self-driving cars
- Augmented reality : Augmented reality (AR) is a method of providing an experience of the natural surroundings with a computer-generated augmentation appropriate to the surroundings
- Medical imaging : X-rays and 3D scans like MRIs are classified into diseases like pneumonia and cancer.
- Intelligent video analytics (IVA) : CCTV cameras are present—in retail venues to understand how shoppers are interacting with products, in factories, airports and transport hubs to track queue lengths and access to restricted areas.
- Manufacturing and Construction
- Retail

Computer Vision Security and Survilance#
- Human Detection Application
- People Movement Analysis Application
- Person Recognition Application
- Weapon Detection Application
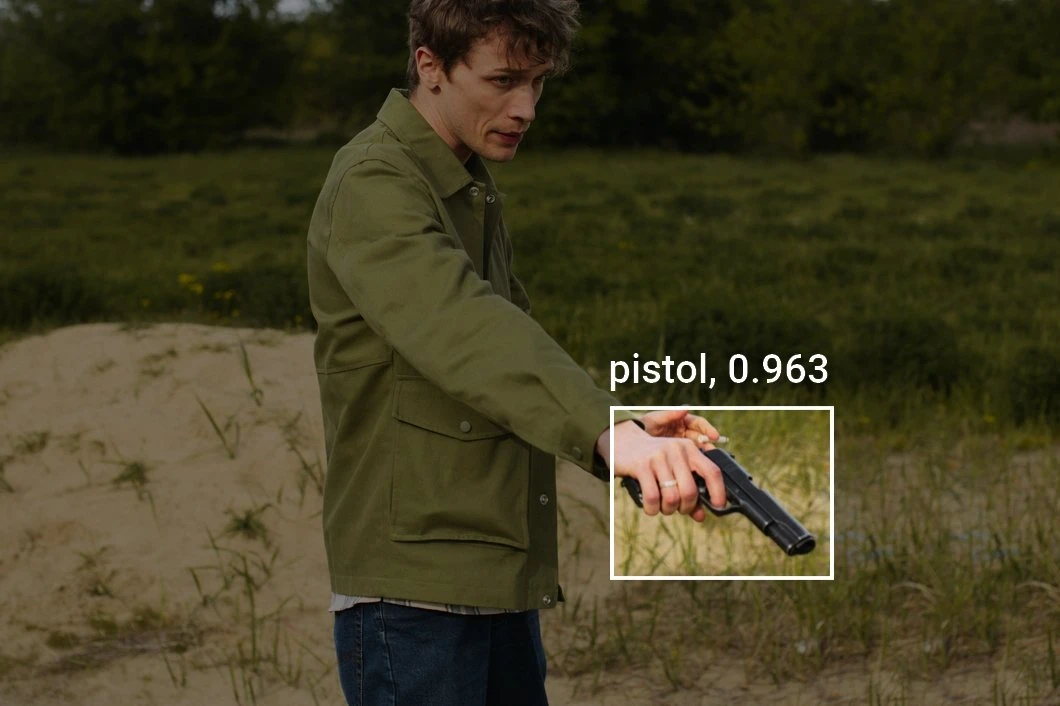

- Human Behavior Understanding Application
- Virtual Fencing Application
- Traffic Incident Detection Application
- Vehicle Surveillance Application
- Vehicle Identification Application

- Traffic Safety Applications Application
- Illegal Activity Detection Application
- Anomaly Detection Application
- Safety Assessment Application
- Infrastructure Security Application
- Emergency Management Application
- Video Summarization Later in this article, we will provide more information about those and more applications. Let’s jump right into the topic!
- Unattended Vehicles
- Unattended Luggage

- Wrong Parking
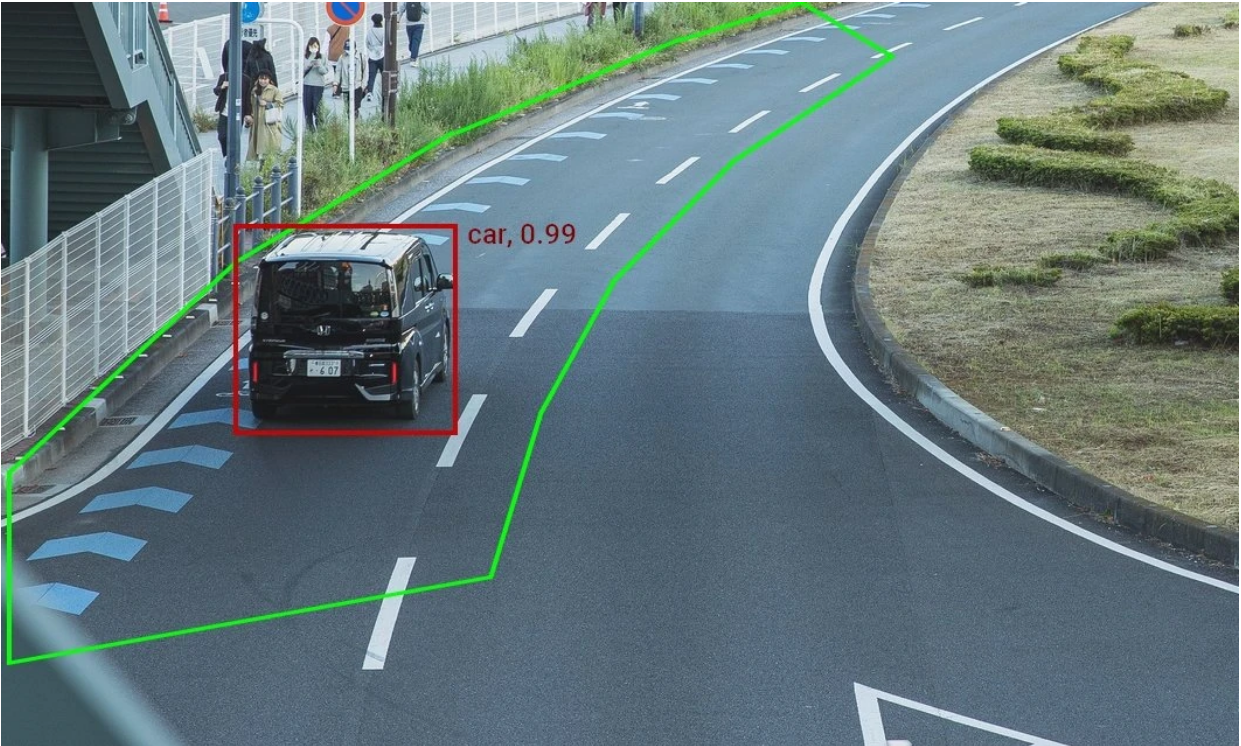
- Parking Lot Detection
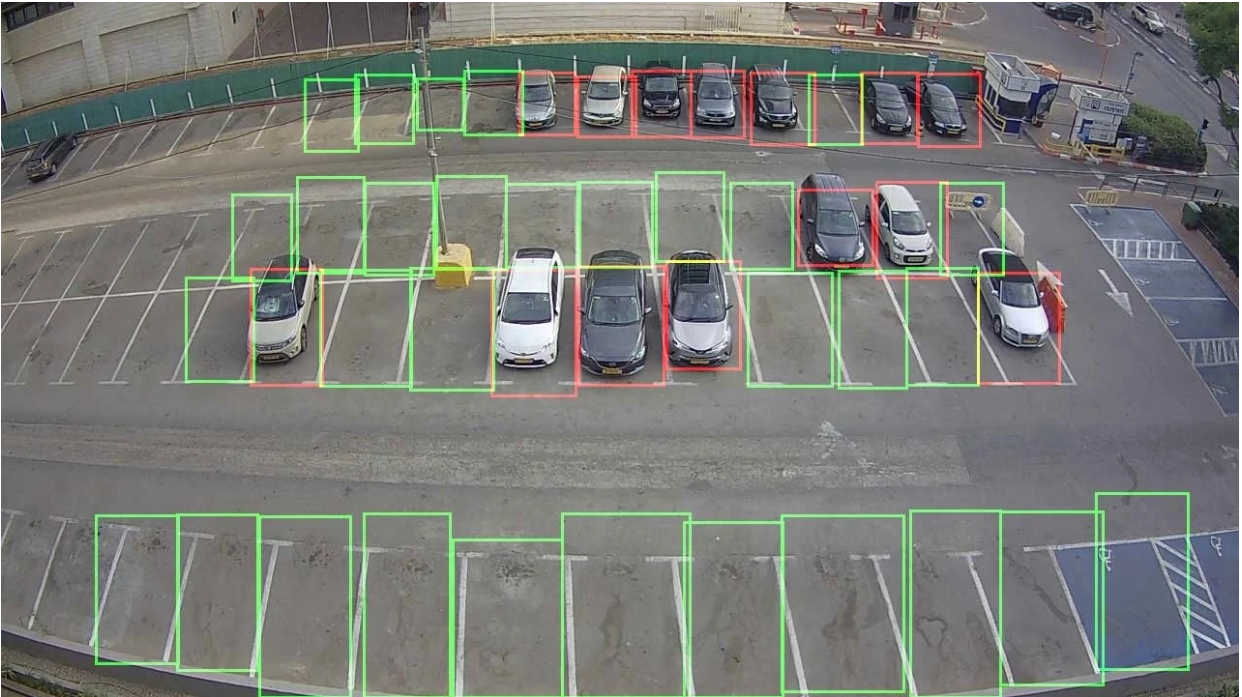

Computer Vision In Healthcare#
- Tumor Detection Application
- Medical Imaging Application
- Cancer Detection Application
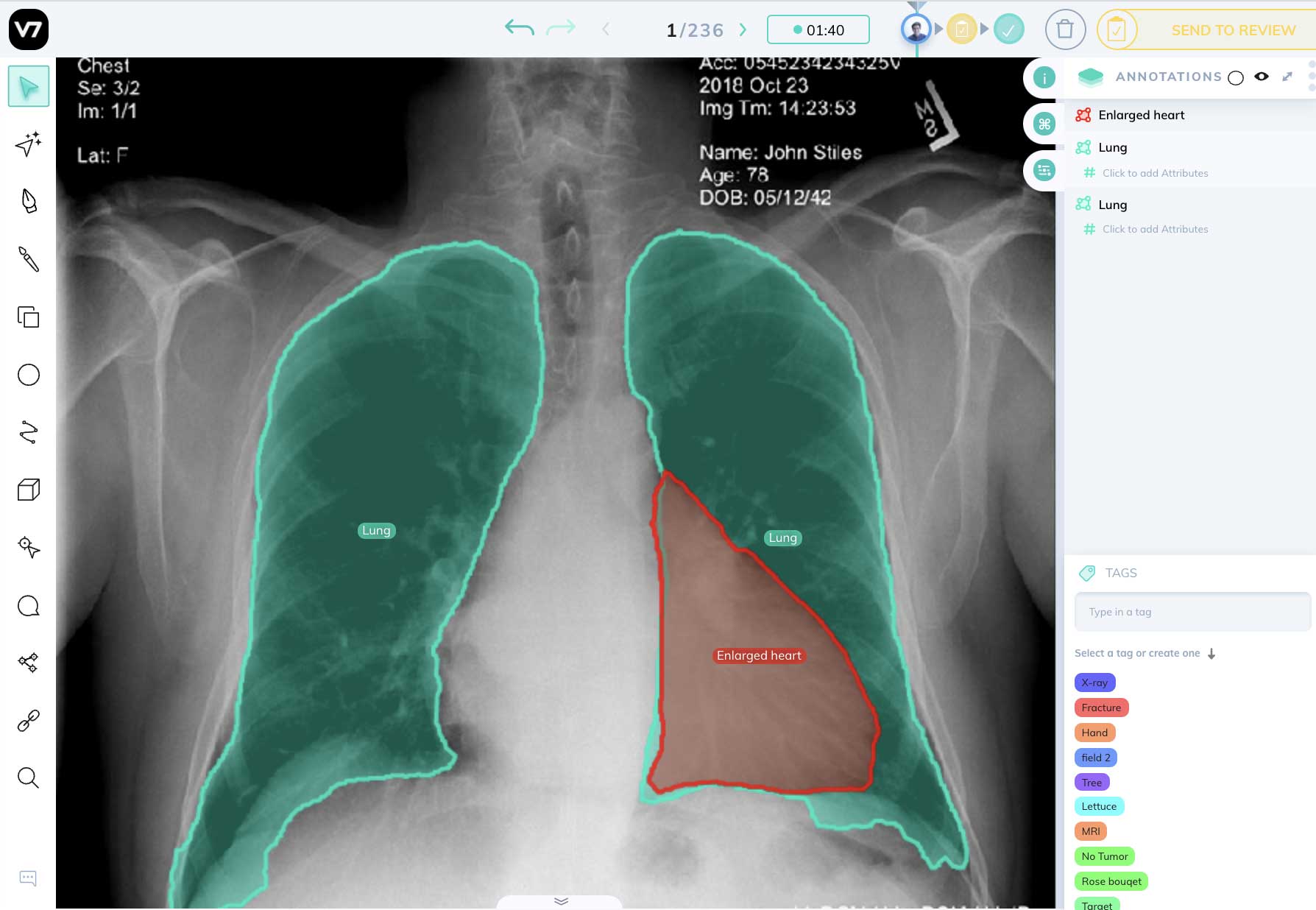
- Medical Training Application
- Combating Covid-19 Application
- Health Monitoring Application
- Machine-assisted Diagnosis Application
- Timely Detection Of Disease Application
- Remote Patient Monitoring Application
- Lean Management in Healthcare
Automotive Industry#
- Type: Automation systems, to conduct tasks otherwise carried out by human operators, reduce human error, as well as production line robots.
- Type: Intelligent systems, to generate insights, early-detect issues that lead to costly business interruptions, facilitate planning, monitor the shop floor and inventory to make better decisions faster.
- Type: Quality control systems, to automatically inspect possible production failures or part defects during assembly or in the final product.
Computer Vision In Manufacturing#
- Pandemic Protective Measures Application
- Quality Inspection and Control Application
- Optimizing Supply Chains Application
- Equipment Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance Application
- Lean Manufacturing Application
- Safety of Workforce and Equipment Application
- Detecting Product Defects Application
- Real-time Barcode Reading Application
- Automated Product Assembly Application
- Maintaining Packaging Standards
Logistics#
- Traceability and tracking of objects Application
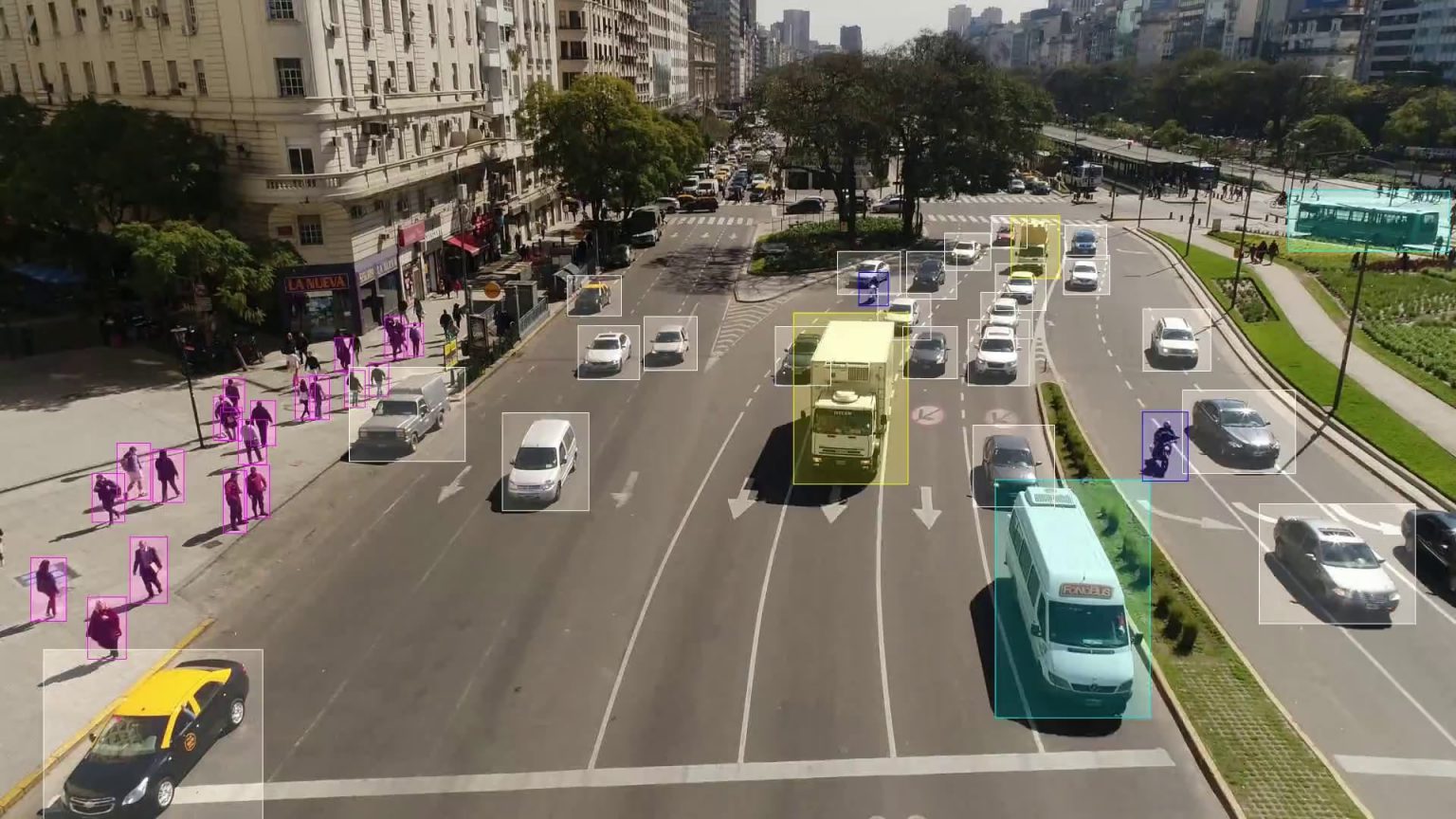

- Volumetric properties of goods Application
- Inspection and quality control of goods Application
- Equipment condition monitoring Application
- Occupancy of storage and traffic areas Application
- Security and protection of infrastructure Application
- Process modeling and simulation Application
- Optimize manual picking and packing Application
- Manually operated handling systems or vehicles Application
- Automated handling systems Application
- Visual documentation and Risk management
- Tracking Warehouse Movements
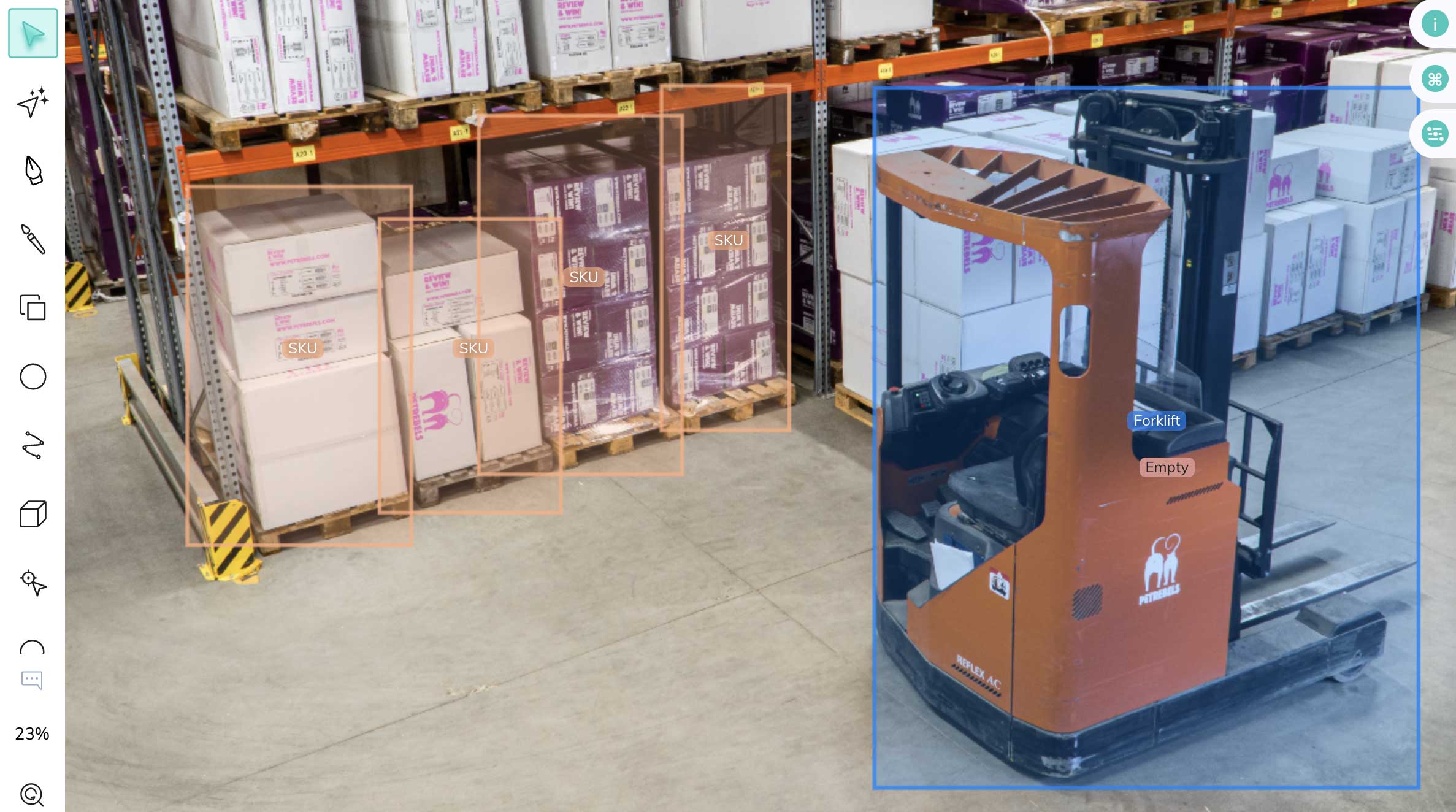

Construction#
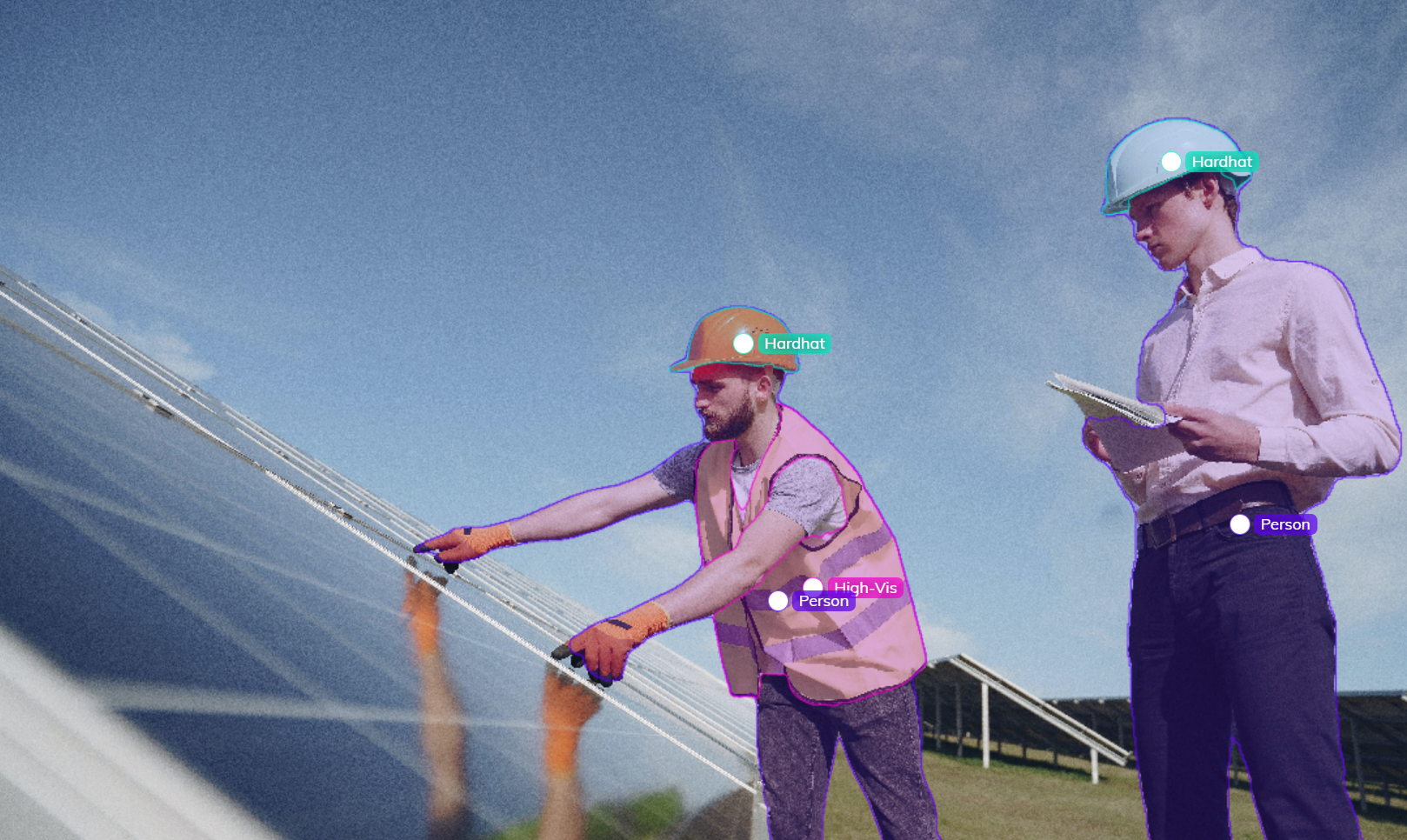

Conclusion#
Human vision is a very precious technology to navigate the world around us, communicate with others, and survive. Similarly, computer vision is an extremely powerful technology to communicate with humans, other machines, and robots. It can perform various tasks as mentioned above. State of the Art (SOTA) computer vision models like DALL-E started challenging human artists. Above mentioned applications are just the tip of the iceberg. You think about any task which you do with your eye-brain coordination and you can perform that with computer vision. In the future, you are going to see many more applications of this technology, and at the same time, this technology will be far superior with advanced algorithms, new hardware, and new application architectures.


Comments: