What is GAN Architecture?#
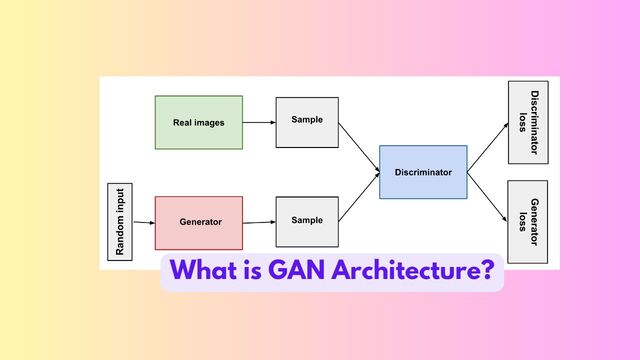
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a powerful class of neural networks that are used for unsupervised learning. It was developed and introduced by Ian J. Goodfellow in 2014. It is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) model that consists of two neural networks: a generator and a discriminator. GANs are used for generative tasks, such as creating realistic images, videos, or even audio.
The generator network in a GAN generates synthetic data, such as images, based on random input or noise. Its goal is to generate samples that resemble the real data it was trained on. Initially, the generator produces low-quality samples, but as it learns, it improves its output.
The discriminator network acts as a judge and tries to distinguish between real and generated samples. It is trained on real data from a specific domain and learns to classify whether an input is real or fake. The discriminator provides feedback to the generator by indicating how well its generated samples resemble the real data. The generator adjusts its parameters weights based on this feedback, aiming to fool the discriminator by generating increasingly realistic samples.
The generator and discriminator are trained together in a competitive manner, where they both learn from each other. The generator learns to produce better samples, while the discriminator learns to become more accurate in distinguishing between real and fake data. This adversarial process continues until the generator becomes proficient at generating highly realistic samples that can fool the discriminator.
GANs have found applications in various domains, including computer vision, image synthesis, style transfer, text-to-image synthesis, and more. They have demonstrated impressive capabilities in generating highly realistic and creative content, making them a popular research area in AI.
GAN Paper Summary#
| # | GAN | Date | Architecture Type | Research Organization | Paper | Author Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AAE Paper | 2016 | GAN | University of Montreal | Adversarial Autoencoder | Alireza Makhzani et al. |
| 2 | cGANs Paper | 2014 | GAN | University of Montreal | Conditional GAN | Mehdi Mirza and Simon Osindero |
| 3 | CycleGAN Paper | 2017 | GAN | University of California, Berkeley | Cycle-Consistent GAN | Jun-Yan Zhu et al. |
| 4 | DCGAN Paper | 2015 | GAN | OpenAI | Deep Convolutional GAN | Alec Radford et al. |
| 5 | DiscoGAN Paper | 2017 | GAN | Seoul National University | DiscoGAN | Taeksoo Kim et al. |
| 6 | EGAN Paper | 2018 | GAN | The Chinese University of Hong Kong | Energy-Based GAN | Zhaoxin Li et al. |
| 7 | GAN Paper | 2014 | GAN | University of Montreal | Generative Adversarial Network | Ian Goodfellow et al. |
| 8 | IsGAN Paper | 2017 | GAN | Carnegie Mellon University | Improved-Synthesis GAN | Zhiting Hu et al. |
| 9 | Large Scale GAN Paper | 2018 | GAN | University of Edinburgh | Large Scale GAN Training for High Fidelity Natural Image Synthesis | Andrew Brock et al. |
| 10 | LSGAN Paper | 2017 | GAN | University of California, Berkeley | Least Squares GAN | Xudong Mao et al. |
| 11 | PGAN Paper | 2017 | GAN | NVIDIA | Progressive Growing of GANs | Tero Karras et al. |
| 12 | pixelRNN Paper | 2016 | GAN | Google DeepMind | Pixel Recurrent Neural Networks | Aaron van den Oord et al. |
| 13 | StackGAN Paper | 2017 | GAN | Carnegie Mellon University | StackGAN | Han Zhang et al. |
| 14 | StyleGAN Paper | 2019 | GAN | NVIDIA | StyleGAN | Tero Karras et al. |
| 15 | text-to-image Paper | 2016 | GAN | University of Michigan | Generative Adversarial Text-to-Image Synthesis | Scott Reed et al. |
| 16 | WGAN Paper | 2017 | GAN | New York University | Wasserstein GAN | Martin Arjovsky et al. |
GAN Capabilities#
| # | GAN | Objective | Summary | NLP Tasks | CV Tasks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AAE | Adversarial Autoencoder | A type of autoencoder that combines generative and discriminative models through an adversarial process. | - | Image Generation |
| 2 | cGANs | Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks | A generative model that can generate samples conditioned on specific input conditions or labels. | - | Image Generation, Image-to-Image Translation |
| 3 | CycleGAN | Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Network | A model for image-to-image translation that learns mappings between two domains without paired training data. | - | Image-to-Image Translation |
| 4 | DCGAN | Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network | A deep convolutional neural network architecture for training generative models using GANs. | - | Image Generation |
| 5 | DiscoGAN | Discover Cross-Domain Relations with GANs | A GAN-based model that learns to map images between different domains without paired training data. | - | Image-to-Image Translation |
| 6 | EGAN | Energy-Based Generative Adversarial Network | A generative model that assigns an energy score to each sample and generates samples with low energy. | - | Image Generation |
| 7 | GAN | Generative Adversarial Network | A framework that consists of a generator and a discriminator network that compete in a two-player min-max game. | - | Image Generation |
| 8 | IsGAN | Improved Wasserstein GAN | A variation of the Wasserstein GAN that improves stability and convergence during training. | - | Image Generation |
| 9 | Large Scale GAN | Large Scale Generative Adversarial Network | GAN models that are designed for generating high-resolution and complex images. | - | Image Generation |
| 10 | LSGAN | Least Squares Generative Adversarial Network | A GAN variant that uses least squares loss functions to improve the training stability and reduce mode collapse. | - | Image Generation |
| 11 | PGAN | Progressive Growing of GANs | A training technique for GANs that gradually increases the size of generated images during training. | - | Image Generation |
| 12 | pixelRNN | Pixel Recurrent Neural Network | A generative model that generates images pixel by pixel using recurrent neural networks. | - | Image Generation |
| 13 | StackGAN | Stack Generative Adversarial Networks | A model that generates high-resolution images in a two-step process, first generating low-resolution images and then refining them. | - | Image Generation |
| 14 | StyleGAN | Style-Based Generative Adversarial Network | A GAN architecture that uses a learned latent space to control the style and appearance of generated images. | - | Image Generation |
| 15 | text-to-image | Text-to-Image Synthesis | Models that generate images from textual descriptions or captions. | Text Generation, Image Generation | Image Generation |
| 16 | WGAN | Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network | A GAN variant that uses Wasserstein distance as a loss function to improve training stability. | - | Image Generation |


Comments: